Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
| Item number | Size | Datasheet | Manual | SDS | Delivery time | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSJ-RQ7416 | 100 µg | - | - |
3 - 10 business days* |
755.00€
|
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
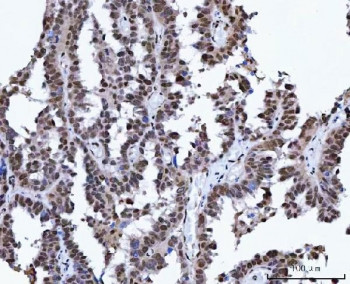
0.5mg/ml if reconstituted with 0.2ml sterile DI water. DNA repair protein XRCC4, also known as... more
Product information "Anti-X-ray repair cross-complementing 4 / XRCC4"
0.5mg/ml if reconstituted with 0.2ml sterile DI water. DNA repair protein XRCC4, also known as X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4 or XRCC4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the XRCC4 gene. In addition to humans, the XRCC4 protein is also expressed in many other metazoans, fungi and in plants. The X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4 is one of several coreproteins involved in the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway to repair DNA double strand breaks(DSBs). Since XRCC4 is the key protein that enables interaction of LigIV to damaged DNA and therefore ligation of the ends, mutations in the XRCC4 gene were found to cause embryonic lethality in mice and developmental inhibition and immunodeficiency in humans. Furthermore, certain mutations in the XRCC4 gene are associated with an increased risk of cancer. Protein function: [DNA repair protein XRCC4]: DNA non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) core factor, required for double-strand break repair and V(D)J recombination (PubMed:10757784, PubMed:10854421, PubMed:17124166, PubMed:16412978, PubMed:8548796, PubMed:25742519, PubMed:12517771, PubMed:17290226, PubMed:22228831, PubMed:25597996, PubMed:25934149, PubMed:26100018, PubMed:26774286). Acts as a scaffold protein that regulates recruitment of other proteins to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) (PubMed:15385968, PubMed:20852255, PubMed:26774286, PubMed:27437582). Associates with NHEJ1/XLF to form alternating helical filaments that bridge DNA and act like a bandage, holding together the broken DNA until it is repaired (PubMed:26100018, PubMed:27437582, PubMed:28500754, PubMed:21775435, PubMed:22287571, PubMed:21768349). The XRCC4-NHEJ1/XLF subcomplex binds to the DNA fragments of a DSB in a highly diffusive manner and robustly bridges two independent DNA molecules, holding the broken DNA fragments in close proximity to one other (PubMed:27437582). The mobility of the bridges ensures that the ends remain accessible for further processing by other repair factors (PubMed:27437582). Plays a key role in the NHEJ ligation step of the broken DNA during DSB repair via direct interaction with DNA ligase IV (LIG4): the LIG4-XRCC4 subcomplex reseals the DNA breaks after the gap filling is completed (PubMed:9242410, PubMed:10757784, PubMed:10854421, PubMed:12517771, PubMed:17290226, PubMed:19837014). XRCC4 stabilizes LIG4, regulates its subcellular localization and enhances LIG4's joining activity (PubMed:9242410, PubMed:10757784, PubMed:10854421, PubMed:12517771, PubMed:17290226, PubMed:21982441, PubMed:22228831). Binding of the LIG4-XRCC4 subcomplex to DNA ends is dependent on the assembly of the DNA-dependent protein kinase complex DNA-PK to these DNA ends (PubMed:10757784, PubMed:10854421). Promotes displacement of PNKP from processed strand break termini (PubMed:20852255, PubMed:28453785). [The UniProt Consortium]
| Keywords: | , X-ray repair cross-complementing 4 Antibody / XRCC4 |
| Supplier: | NSJ Bioreagents |
| Supplier-Nr: | RQ7416 |
Properties
| Application: | WB, IHC (paraffin), IF, FC, Direct ELISA |
| Antibody Type: | Polyclonal |
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| Species reactivity: | human |
| Immunogen: | E. coli-derived recombinant human protein (amino acids M1-D255) |
| Format: | Purified |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K10886 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | Q13426 | Matching products |
| Gene ID | GeneID 7518 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | +4°C |
| Shipping: | +4°C (International: +4°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed