Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
| Item number | Size | Datasheet | Manual | SDS | Delivery time | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSJ-V9259SAF-100UG | 100 µg | - | - |
3 - 10 business days* |
752.00€
|
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
1 mg/ml in 1X PBS, BSA free, sodium azide free. The exon junction complex (EJC) is a multiprotein... more
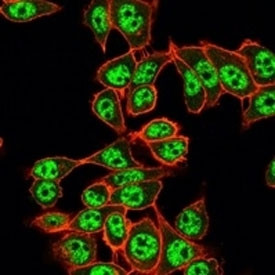
Product information "Anti-RBM8A/Y14, clone PCRP-RBM8A-1B4"
1 mg/ml in 1X PBS, BSA free, sodium azide free. The exon junction complex (EJC) is a multiprotein complex that assembles approximately 20-24 nucleotides upstream of exon-exon junctions in pre-mRNAs. It is involved in mRNA export, cytoplasmic localization, and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Members of the EJC include Y14, Aly/REF, Magoh, RNPS1, SRm160, and DEK. Aly/REF, Magoh, and Y14, identified as RBM8 in mouse and rat, make up the core of the EJC, and these proteins remain stably bound to spliced mRNAs in the cytoplasm until they are translated. Therefore, Y14, Aly/REF, and Magoh have the ability to communicate to the cytoplasm the processing history of the mRNA, including the position of the removed introns. The gene encoding human Y14 encodes three transcripts. Y14 is a ubiquitously expressed protein. Although Y14 shuttles to the cytoplasm, it is predominantly detected in the nucleus and is co-localized with oskar mRNA at the posterior pole of the cell. Protein function: Required for pre-mRNA splicing as component of the spliceosome (PubMed:28502770, PubMed:29301961). Core component of the splicing-dependent multiprotein exon junction complex (EJC) deposited at splice junctions on mRNAs. The EJC is a dynamic structure consisting of core proteins and several peripheral nuclear and cytoplasmic associated factors that join the complex only transiently either during EJC assembly or during subsequent mRNA metabolism. The EJC marks the position of the exon-exon junction in the mature mRNA for the gene expression machinery and the core components remain bound to spliced mRNAs throughout all stages of mRNA metabolism thereby influencing downstream processes including nuclear mRNA export, subcellular mRNA localization, translation efficiency and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). The MAGOH-RBM8A heterodimer inhibits the ATPase activity of EIF4A3, thereby trapping the ATP-bound EJC core onto spliced mRNA in a stable conformation. The MAGOH-RBM8A heterodimer interacts with the EJC key regulator PYM1 leading to EJC disassembly in the cytoplasm and translation enhancement of EJC-bearing spliced mRNAs by recruiting them to the ribosomal 48S preinitiation complex. Its removal from cytoplasmic mRNAs requires translation initiation from EJC-bearing spliced mRNAs. Associates preferentially with mRNAs produced by splicing. Does not interact with pre-mRNAs, introns, or mRNAs produced from intronless cDNAs. Associates with both nuclear mRNAs and newly exported cytoplasmic mRNAs. The MAGOH-RBM8A heterodimer is a component of the nonsense mediated decay (NMD) pathway. Involved in the splicing modulation of BCL2L1/Bcl-X (and probably other apoptotic genes), specifically inhibits formation of proapoptotic isoforms such as Bcl- X(S), the function is different from the established EJC assembly. [The UniProt Consortium]
| Keywords: | Anti-RBM8, Anti-RBM8A, Anti-BOV-1, Anti-HSPC114, Anti-Binder of OVCA1-1, Anti-RNA-binding protein 8A, Anti-Ribonucleoprotein RBM8A, Anti-RNA-binding protein Y14, Anti-RNA-binding motif protein 8A, RBM8A/Y14 Antibody |
| Supplier: | NSJ Bioreagents |
| Supplier-Nr: | V9259SAF |
Properties
| Application: | FC, IF, WB |
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal |
| Clone: | PCRP-RBM8A-1B4 |
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | Mouse |
| Species reactivity: | human |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant full-length human RBM8A protein |
| Format: | Purified |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K12876 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | Q9Y5S9 | Matching products |
| Gene ID | GeneID 9939 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | -20°C |
| Shipping: | -20°C (International: -20°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed