Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
| Item number | Size | Datasheet | Manual | SDS | Delivery time | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSJ-RQ7125 | 100 µg | - | - |
3 - 10 business days* |
755.00€
|
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
0.5mg/ml if reconstituted with 0.2ml sterile DI water. Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that... more
Product information "Anti-KPNB1 / Importin subunit beta 1, clone 3I11F2"
0.5mg/ml if reconstituted with 0.2ml sterile DI water. Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNB1 gene. Nucleocytoplasmic transport, a signal- and energy-dependent process, takes place through nuclear pore complexes embedded in the nuclear envelope. The import of proteins containing a nuclear localization signal (NLS) requires the NLS import receptor, a heterodimer of importin alpha and beta subunits also known as karyopherins. Importin alpha binds the NLS-containing cargo in the cytoplasm and importin beta docks the complex at the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore complex. In the presence of nucleoside triphosphates and the small GTP binding protein Ran, the complex moves into the nuclear pore complex and the importin subunits dissociate. Importin alpha enters the nucleoplasm with its passenger protein and importin beta remains at the pore. Interactions between importin beta and the FG repeats of nucleoporins are essential in translocation through the pore complex. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the importin beta family. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Protein function: Functions in nuclear protein import, either in association with an adapter protein, like an importin-alpha subunit, which binds to nuclear localization signals (NLS) in cargo substrates, or by acting as autonomous nuclear transport receptor. Acting autonomously, serves itself as NLS receptor. Docking of the importin/substrate complex to the nuclear pore complex (NPC) is mediated by KPNB1 through binding to nucleoporin FxFG repeats and the complex is subsequently translocated through the pore by an energy requiring, Ran-dependent mechanism. At the nucleoplasmic side of the NPC, Ran binds to importin-beta and the three components separate and importin-alpha and -beta are re-exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where GTP hydrolysis releases Ran from importin. The directionality of nuclear import is thought to be conferred by an asymmetric distribution of the GTP- and GDP-bound forms of Ran between the cytoplasm and nucleus. Mediates autonomously the nuclear import of ribosomal proteins RPL23A, RPS7 and RPL5 (PubMed:11682607). In association with IPO7, mediates the nuclear import of H1 histone. In vitro, mediates nuclear import of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 histones. In case of HIV-1 infection, binds and mediates the nuclear import of HIV-1 Rev. Imports SNAI1 and PRKCI into the nucleus. [The UniProt Consortium]
| Keywords: | Anti-KPNB1, Anti-NTF97, Anti-PTAC97, Anti-Importin-90, Anti-Nuclear factor p97, Anti-Importin subunit beta-1, Anti-Karyopherin subunit beta-1, Anti-Pore targeting complex 97 kDa subunit, KPNB1 Antibody / Importin subunit beta 1 |
| Supplier: | NSJ Bioreagents |
| Supplier-Nr: | RQ7125 |
Properties
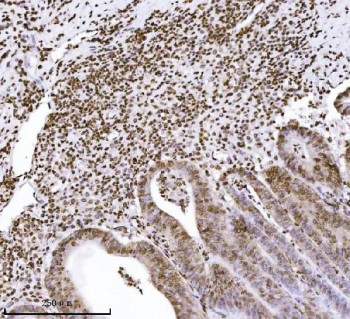
| Application: | WB, IHC (paraffin), IF, FC |
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal |
| Clone: | 3I11F2 |
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | Mouse |
| Species reactivity: | human, mouse, rat |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant human protein (amino acids E8-A876) |
| Format: | Purified |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K14293 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | Q14974 | Matching products |
| Gene ID | GeneID 3837 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | +4°C |
| Shipping: | +4°C (International: +4°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed