Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
This gene encodes one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing... more
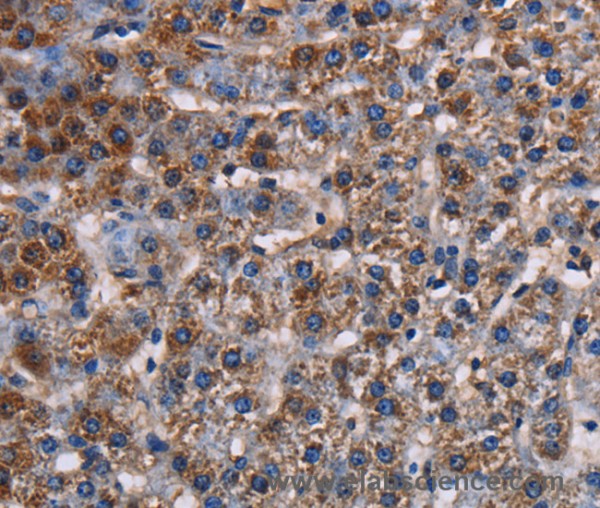
Product information "Anti-KCNK1"
This gene encodes one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore-forming P domains. The product of this gene has not been shown to be a functional channel, however, it may require other non-pore-forming proteins for activity. Protein function: Ion channel that contributes to passive transmembrane potassium transport and to the regulation of the resting membrane potential in brain astrocytes, but also in kidney and in other tissues (PubMed:15820677, PubMed:21653227). Forms dimeric channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel is selective for K(+) ions at physiological potassium concentrations and at neutral pH, but becomes permeable to Na(+) at subphysiological K(+) levels and upon acidification of the extracellular medium (PubMed:21653227, PubMed:22431633). The homodimer has very low potassium channel activity, when expressed in heterologous systems, and can function as weakly inward rectifying potassium channel (PubMed:8605869, PubMed:8978667, PubMed:15820677, PubMed:21653227, PubMed:22431633, PubMed:23169818, PubMed:25001086). Channel activity is modulated by activation of serotonin receptors. Heterodimeric channels containing KCNK1 and KCNK2 have much higher activity, and may represent the predominant form in astrocytes. Heterodimeric channels containing KCNK1 and KCNK3 or KCNK9 have much higher activity (PubMed:23169818). Heterodimeric channels formed by KCNK1 and KCNK9 may contribute to halothane- sensitive currents (PubMed:23169818). Mediates outward rectifying potassium currents in dentate gyrus granule cells and contributes to the regulation of their resting membrane potential. Contributes to the regulation of action potential firing in dentate gyrus granule cells and down-regulates their intrinsic excitability. In astrocytes, the heterodimer formed by KCNK1 and KCNK2 is required for rapid glutamate release in response to activation of G-protein coupled receptors, such as F2R and CNR1. Required for normal ion and water transport in the kidney. Contributes to the regulation of the resting membrane potential of pancreatic beta cells. The low channel activity of homodimeric KCNK1 may be due to sumoylation (PubMed:15820677, PubMed:20498050, PubMed:23169818). The low channel activity may be due to rapid internalization from the cell membrane and retention in recycling endosomes (PubMed:19959478). [The UniProt Consortium]
| Keywords: | Anti-KCNK1, Anti-Potassium channel K2P1, Anti-Potassium channel KCNO1, Anti-Potassium channel subfamily K member 1, Anti-Inward rectifying potassium channel protein TWIK-1, KCNK1 Polyclonal Antibody |
| Supplier: | Elabscience |
| Supplier-Nr: | E-AB-11347 |
Properties
| Application: | IHC, ELISA |
| Antibody Type: | Polyclonal |
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| Species reactivity: | human, mouse, rat |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human KCNK1 |
| Format: | Purified |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K04912 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | O00180 | Matching products |
| Gene ID | GeneID 3775 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | -20°C |
| Shipping: | 4°C (International: -20°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed