Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
| Item number | Size | Datasheet | Manual | SDS | Delivery time | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSJ-F47586-0.08ML | 80 µl | - | - |
3 - 10 business days* |
326.00€
|
||
| NSJ-F47586-0.4ML | 400 µl | - | - |
3 - 10 business days* |
702.00€
|
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
In 1X PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.09% sodium azide. NFKB1 or NFKB2 is bound to REL, RELA, or RELB to form... more
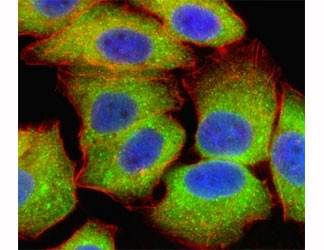
Product information "Anti-RELA"
In 1X PBS, pH 7.4, with 0.09% sodium azide. NFKB1 or NFKB2 is bound to REL, RELA, or RELB to form the NFKB complex. The p50 (NFKB1)/p65 (RELA) heterodimer is the most abundant form of NFKB. The NFKB complex is inhibited by I-kappa-B proteins (NFKBIA or NFKBIB), which inactivates NFKB by trapping it in the cytoplasm. Phosphorylation of serine residues on the I-kappa-B proteins by kinases (IKBKA or IKBKB) marks them for destruction via the ubiquitination pathway, thereby allowing activation of the NFKB complex. Activated NFKB complex translocates into the nucleus and binds DNA at kappa-B-binding motifs. [OMIM] Protein function: NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and p65-c-Rel complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p65-p65 complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. The inhibitory effect of I-kappa-B upon NF-kappa-B the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with p65. p65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappa-B complex. Associates with chromatin at the NF-kappa-B promoter region via association with DDX1. Essential for cytokine gene expression in T-cells (PubMed:15790681). [The UniProt Consortium]
| Keywords: | Anti-RELA, Anti-NFKB3, Anti-Transcription factor p65, Anti-Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit, Anti-Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 3, RELA Antibody |
| Supplier: | NSJ Bioreagents |
| Supplier-Nr: | F47586 |
Properties
| Application: | WB, IF, ELISA |
| Antibody Type: | Polyclonal |
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| Species reactivity: | human |
| Immunogen: | A portion of amino acids 166-195 from the human protein was used as the immunogen for this RELA antibody. |
| Format: | Purified |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K04735 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | Q04206 | Matching products |
| Gene ID | GeneID 5970 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | -20°C |
| Shipping: | +4°C (International: +4°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed