Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
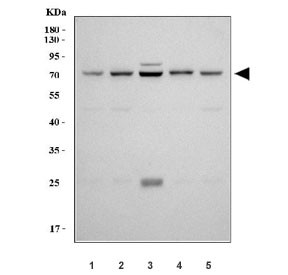
| Item number | Size | Datasheet | Manual | SDS | Delivery time | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSJ-R32712 | 100 µg | - | - |
3 - 10 business days* |
772.00€
|
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
0.5mg/ml if reconstituted with 0.2ml sterile DI water. Cyclooxygenase (Cox) is the key enzyme in... more
Product information "Anti-COX2 / PTGS2"
0.5mg/ml if reconstituted with 0.2ml sterile DI water. Cyclooxygenase (Cox) is the key enzyme in conversion of arachidonic acid to PGs, and two isoforms, Cox-1 and Cox-2, have been identified. Cox-2 gene encodes an inducible prostaglandin synthase enzyme that is overexpressed in adenocarcinomas and other tumors. Deletion of the murine Cox-2 gene in Min mice reduced the incidence of intestinal tumors, suggesting that it is required for tumorigenesis. This gene is localized to sites associated with retinal blood vessels, and plays an important role in blood vessel formation in the retina. And the glucocorticoid receptor suppression of COX-2 is also crucial for curtailing lethal immune activation, and suggests new therapeutic approaches for regulation of T-cell-mediated inflammatory diseases. Protein function: Dual cyclooxygenase and peroxidase in the biosynthesis pathway of prostanoids, a class of C20 oxylipins mainly derived from arachidonate ((5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate, AA, C20:4(n-6)), with a particular role in the inflammatory response (PubMed:7947975, PubMed:7592599, PubMed:9261177, PubMed:16373578, PubMed:22942274, PubMed:26859324, PubMed:27226593, PubMed:11939906, PubMed:19540099). The cyclooxygenase activity oxygenates AA to the hydroperoxy endoperoxide prostaglandin G2 (PGG2), and the peroxidase activity reduces PGG2 to the hydroxy endoperoxide prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), the precursor of all 2-series prostaglandins and thromboxanes (PubMed:7947975, PubMed:7592599, PubMed:9261177, PubMed:16373578, PubMed:22942274, PubMed:26859324, PubMed:27226593). This complex transformation is initiated by abstraction of hydrogen at carbon 13 (with S-stereochemistry), followed by insertion of molecular O2 to form the endoperoxide bridge between carbon 9 and 11 that defines prostaglandins. The insertion of a second molecule of O2 (bis-oxygenase activity) yields a hydroperoxy group in PGG2 that is then reduced to PGH2 by two electrons (PubMed:7947975, PubMed:7592599, PubMed:9261177, PubMed:16373578, PubMed:22942274, PubMed:26859324, PubMed:27226593). Similarly catalyzes successive cyclooxygenation and peroxidation of dihomo-gamma-linoleate (DGLA, C20:3(n-6)) and eicosapentaenoate (EPA, C20:5(n-3)) to corresponding PGH1 and PGH3, the precursors of 1- and 3- series prostaglandins (PubMed:11939906, PubMed:19540099). In an alternative pathway of prostanoid biosynthesis, converts 2-arachidonoyl lysophopholipids to prostanoid lysophopholipids, which are then hydrolyzed by intracellular phospholipases to release free prostanoids (PubMed:27642067). Metabolizes 2-arachidonoyl glycerol yielding the glyceryl ester of PGH2, a process that can contribute to pain response (PubMed:22942274). Generates lipid mediators from n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) via a lipoxygenase-type mechanism. Oxygenates PUFAs to hydroperoxy compounds and then reduces them to corresponding alcohols (PubMed:11034610, PubMed:11192938, PubMed:9048568, PubMed:9261177). Plays a role in the generation of resolution phase interaction products (resolvins) during both sterile and infectious inflammation (PubMed:12391014). Metabolizes docosahexaenoate (DHA, C22:6(n-3)) to 17R-HDHA, a precursor of the D- series resolvins (RvDs) (PubMed:12391014). As a component of the biosynthetic pathway of E-series resolvins (RvEs), converts eicosapentaenoate (EPA, C20:5(n-3)) primarily to 18S-HEPE that is further metabolized by ALOX5 and LTA4H to generate 18S-RvE1 and 18S- RvE2 (PubMed:21206090). In vascular endothelial cells, converts docosapentaenoate (DPA, C22:5(n-3)) to 13R-HDPA, a precursor for 13- series resolvins (RvTs) shown to activate macrophage phagocytosis during bacterial infection (PubMed:26236990). In activated leukocytes, contributes to oxygenation of hydroxyeicosatetraenoates (HETE) to diHETES (5,15-diHETE and 5,11-diHETE) (PubMed:22068350, PubMed:26282205). Can also use linoleate (LA, (9Z,12Z)- octadecadienoate, C18:2(n-6)) as substrate and produce hydroxyoctadecadienoates (HODEs) in a regio- and stereospecific manner, being (9R)-HODE ((9R)-hydroxy-(10E,12Z)-octadecadienoate) and (13S)- HODE ((13S)-hydroxy-(9Z,11E)-octadecadienoate) its major products. During neuroinflammation, plays a role in neuronal secretion of specialized preresolving mediators (SPMs) 15R-lipoxin A4 that regulates phagocytic microglia. [The UniProt Consortium]
| Keywords: | Anti-COX-2, Anti-PHS II, Anti-PGHS-2, Anti-PGH synthase 2, Anti-Cyclooxygenase-2, Anti-Prostaglandin H2 synthase 2, Anti-Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2, Anti-Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2, COX2 Antibody / PTGS2 |
| Supplier: | NSJ Bioreagents |
| Supplier-Nr: | R32712 |
Properties
| Application: | WB |
| Antibody Type: | Polyclonal |
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| Species reactivity: | human |
| Immunogen: | amino acids 365-397 (AEFNTLYHWHPLLPDTFQIHDQKYNYQQFIYNN) from the human protein |
| Format: | Purified |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K11987 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | P35354 | Matching products |
| Gene ID : | GeneID 5743 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | +4°C |
| Shipping: | +4°C (International: +4°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed


