Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
The protein encoded by this gene is a major apoprotein of the chylomicron. It binds to a specific... more
Product information "Anti-APOE"
The protein encoded by this gene is a major apoprotein of the chylomicron. It binds to a specific liver and peripheral cell receptor, and is essential for the normal catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein constituents. This gene maps to chromosome 19 in a cluster with the related apolipoprotein C1 and C2 genes. Mutations in this gene result in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia, or type III hyperlipoproteinemia (HLP III), in which increased plasma cholesterol and triglycerides are the consequence of impaired clearance of chylomicron and VLDL remnants. Protein function: APOE is an apolipoprotein, a protein associating with lipid particles, that mainly functions in lipoprotein-mediated lipid transport between organs via the plasma and interstitial fluids (PubMed:6860692, PubMed:1911868, PubMed:14754908). APOE is a core component of plasma lipoproteins and is involved in their production, conversion and clearance (PubMed:6860692, PubMed:2762297, PubMed:1911868, PubMed:1917954, PubMed:9395455, PubMed:14754908, PubMed:23620513). Apoliproteins are amphipathic molecules that interact both with lipids of the lipoprotein particle core and the aqueous environment of the plasma (PubMed:6860692, PubMed:2762297, PubMed:9395455). As such, APOE associates with chylomicrons, chylomicron remnants, very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL) but shows a preferential binding to high-density lipoproteins (HDL) (PubMed:6860692, PubMed:1911868). It also binds a wide range of cellular receptors including the LDL receptor/LDLR, the LDL receptor-related proteins LRP1, LRP2 and LRP8 and the very low-density lipoprotein receptor/VLDLR that mediate the cellular uptake of the APOE-containing lipoprotein particles (PubMed:2762297, PubMed:1917954, PubMed:7768901, PubMed:8939961, PubMed:12950167, PubMed:20030366, PubMed:2063194, PubMed:8756331, PubMed:20303980, PubMed:1530612, PubMed:7635945). Finally, APOE has also a heparin-binding activity and binds heparan-sulfate proteoglycans on the surface of cells, a property that supports the capture and the receptor-mediated uptake of APOE-containing lipoproteins by cells (PubMed:9395455, PubMed:9488694, PubMed:23676495, PubMed:7635945). A main function of APOE is to mediate lipoprotein clearance through the uptake of chylomicrons, VLDLs, and HDLs by hepatocytes (PubMed:1911868, PubMed:1917954, PubMed:9395455, PubMed:23676495, PubMed:29516132). APOE is also involved in the biosynthesis by the liver of VLDLs as well as their uptake by peripheral tissues ensuring the delivery of triglycerides and energy storage in muscle, heart and adipose tissues (PubMed:2762297, PubMed:29516132). By participating to the lipoprotein-mediated distribution of lipids among tissues, APOE plays a critical role in plasma and tissues lipid homeostasis (PubMed:2762297, PubMed:1917954, PubMed:29516132). APOE is also involved in two steps of reverse cholesterol transport, the HDLs- mediated transport of cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver, and thereby plays an important role in cholesterol homeostasis (PubMed:9395455, PubMed:14754908, PubMed:23620513). First, it is functionally associated with ABCA1 in the biogenesis of HDLs in tissues (PubMed:14754908, PubMed:23620513). Second, it is enriched in circulating HDLs and mediates their uptake by hepatocytes (PubMed:9395455). APOE also plays an important role in lipid transport in the central nervous system, regulating neuron survival and sprouting (PubMed:8939961, PubMed:25173806). APOE in also involved in innate and adaptive immune responses, controlling for instance the survival of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. APOE, may also play a role in transcription regulation through a receptor-dependent and cholesterol- independent mechanism, that activates MAP3K12 and a non-canonical MAPK signal transduction pathway that results in enhanced AP-1- mediated transcription of APP (PubMed:28111074). [The UniProt Consortium]
| Keywords: | Anti-APOE, Anti-Apo-E, Anti-Apolipoprotein E, APOE Polyclonal Antibody |
| Supplier: | Elabscience |
| Supplier-Nr: | E-AB-62006 |
Properties
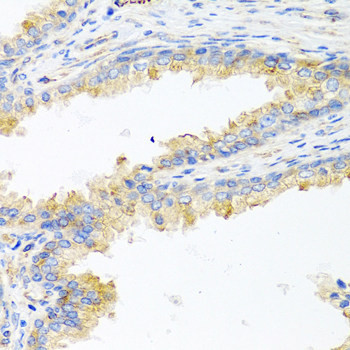
| Application: | IHC |
| Antibody Type: | Polyclonal |
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | Rabbit |
| Species reactivity: | human, mouse |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human ApoE |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K04524 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | P02649 | Matching products |
| Gene ID | GeneID 348 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | -20°C |
| Shipping: | 4°C (International: -20°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed