Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
| Item number | Size | Datasheet | Manual | SDS | Delivery time | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cay32015-100 | 100 µg | - |
6 - 10 business days* |
439.00€
|
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
CD1b is a member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins and is an MHC class I-like... more
Product information "CD1b Long Isoform Extracellular Ligand-binding Domain (human, recombinant)"
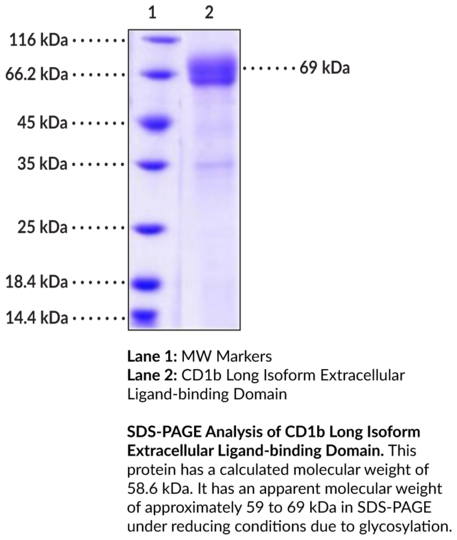
CD1b is a member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins and is an MHC class I-like molecule that presents lipid antigens to T cells. Alternative splicing of CD1B produces one full-length isoform, CD1b long, and one short isoform. CD1b long exists as a tetramer where each monomer is composed of a transmembrane CD1 heavy chain that contains three extracellular domains (alpha1-alpha3), which associate with beta2-microglobulin to form a lipid-binding groove, as well as a cytoplasmic tail that contains a YXXZ endosomal sorting motif and interacts with the chaperone proteins AP-2 and AP-3 to direct CD1b intracellular trafficking. The CD1b short isoform lacks the endosomal sorting motif and is confined to the cell surface. CD1b expression is induced in antigen-presenting cells by bacteria or toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), IL-1beta, or GM-CSF stimulation and functions to present a variety of lipid antigens to T cells. CD1b is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and is transported to the cell membrane where it expresses self-lipids, such as sphingolipids and phospholipids. It is then internalized and localizes to the late endosome or lysosome where it exchanges self-lipids for pathogen-derived lipids, including mycolates and lipoglycans, prior to being re-expressed on the cell surface for T cell presentation. CD1b protein levels are increased in skin lesions from patients with leprosy, in lung granulomas from patients with tuberculosis, and in postmortem-derived brain lesions from patients with multiple sclerosis. CD1B SNPs have been found in patients with prostate cancer. Cayman's CD1b Long Isoform Extracellular Ligand-binding Domain (human, recombinant) protein is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer, comprised of CD1b Long Isoform Extracellular Ligand-binding Domain (amino acids 18-303) fused to human IgG1 Fc at its C-terminus, consists of 527 amino acids, has a calculated molecular weight of 58.6 kDa, and a predicted N-terminus of Ser18. As a result of glycosylation, the monomer migrates at approximately 59 to 69 kDa by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.Synonyms: R1. Purity: >88% estimated by SDS-PAGE. Endotoxin Testing: < 1.0 EU/µg, determined by the LAL endotoxin assay. Source: Recombinant C-terminal human IgG1 Fc-His-tagged CD1b expressed in HEK293 cells. Amino Acids: 18-303. MW: 58.6 kDa. Formulation: (Request formulation change), Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. UniProt Accession #: P29016.
| Keywords: | CD1B, CD1b, CD1b, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1b, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1b |
| Supplier: | Cayman Chemical |
| Supplier-Nr: | 32015 |
Properties
| Conjugate: | No |
| Purity: | >88% estimated by SDS-PAGE |
| Format: | Lyophilized |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K06448 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | P29016 | Matching products |
| Gene ID | GeneID 910 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | -80°C |
| Shipping: | -80°C (International: -80°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed