Biomol offers more than 625.000 products for life science research. Many of these products are used to enable new discoveries and are featured in a wide range of peer-reviewed publications. But which are the most highly cited products of all time? This list introduces the top 10 most cited products on Biomol.
Through our partnership with CiteAb, we are now able to provide our customers with high-quality reagent product citations for antibodies, proteins, biochemicals, and assays. The product citations tab on each product page lists publications which use individual reagents, providing real world examples of products used in literature and information to help plan your experiments.
| Product | Type | Company | Citations (20.04.2021) |
| Anti-Red Fluorescent Protein (RFP) | Antibody | Rockland Immunochemicals | 478 |
| Anti-phospho-RPA32 (Ser4/Ser8) | Antibody | Bethyl Laboratories | 250 |
| Prostaglandin E2 | Small molecule | Cayman Chemical | 199 |
| Rosiglitazone | Small molecule | Cayman Chemical | 185 |
| Anti-SMC1 | Antibody | Bethyl Laboratories | 181 |
| Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) | Antibody | Rockland Immunochemicals | 183 |
| Anti-Mouse EBI-3, clone V1.4C4.22 | Antibody | Rockland Immunochemicals | 178 |
| Anti-53BP1 | Antibody | Bethyl Laboratories | 174 |
| Rapamycin | Small molecule | LC Laboratories | 176 |
| Anti-phospho-KAP-1 | Antibody | Bethyl Laboratories | 150 |
Anti-Red Fluorescent Protein (RFP)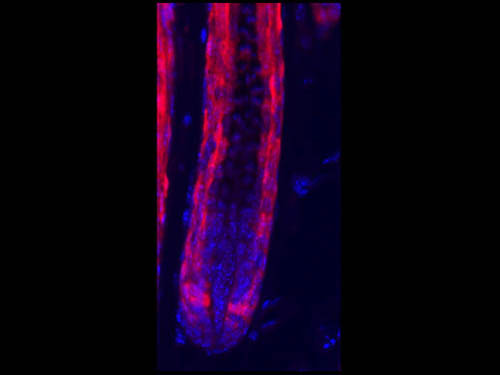
The red fluorescent protein (RFP) is one of the most common biomarkers. It is used to visualize cellular processes, localize proteins, and to confirm expression of transgenic constructs. Upon excitation with blue light, a bright red fluorescence can be detected. This anti-RFP antibody can be used in a variety of applications to detect or purify different RFP fusion proteins. Methods include immunofluorescence (as seen in the image to the right), immunoprecipitation, and western blotting.
Anti-phospho-RPA32 (Ser4/Ser8)
This antibody specifically binds to the 32 kDa subunit of replication protein A (RPA), when it is phosphorylated at serine 4 /serine 8. Certain phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinases like the DNA-dependent protein kinase phosphorylate are responsible for this phosphorylation in response to replication stress. RPA itself binds single-stranded DNA and has a crucial role in DNA replication, DNA repair, and checkpoint signaling. Therefore, this antibody is a great marker to assess the replication process in cells and detect single-stranded DNA in eukaryotic cells.
Prostaglandin E2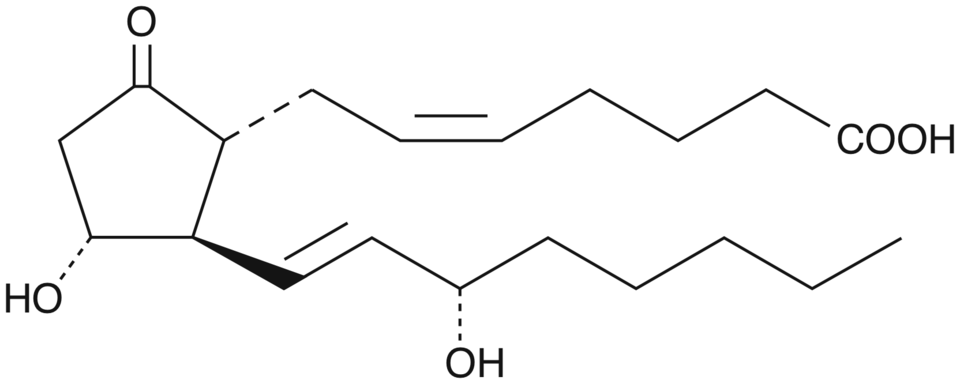
Prostaglandin E2 (chemical structure in the image to the right) is a hormone found in humans and animals. Upon binding to one of the four G protein-coupled receptors, EP1-EP4 prostaglandin E2 causes different downstream effects depending on the receptor subtype and tissue. It influences inflammation, fertility and parturition, gastric mucosal integrity, and immune modulation. Therefore, this compound is used in a variety of different experimental set ups and put to clinical use to terminate pregnancies, induce labor, or treat newborns with congenital heart disease.
Rosiglitazone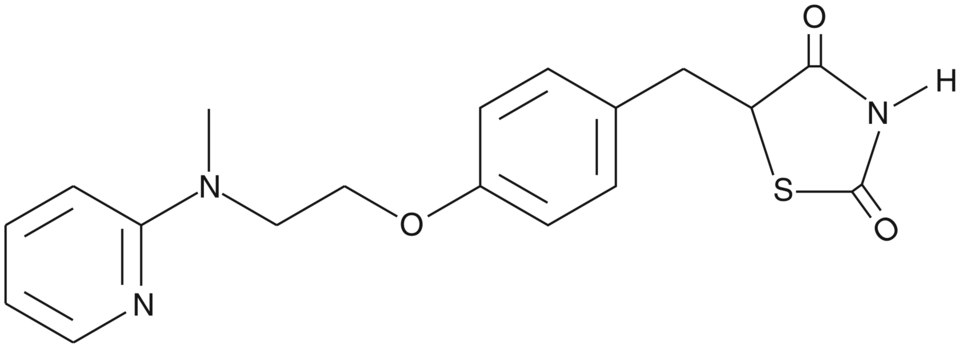
The applications of rosiglitazone (chemical structure in the image to the right) are based on its interactions with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). It acts as a ligand to activate those receptors, which functions as transcription factors. Based on this interaction and downstream transcription of genes involved in insulin sensitivity, rosiglitazone was used as a drug against type 2 diabetes (nowadays the administration is disputed due to potential cardiac side effects). For research applications, rosiglitazone is used in various PPAR reporter assays to induce stem cell differentiation to adipocytes and for different PPAR-related animal models.
Anti-SMC1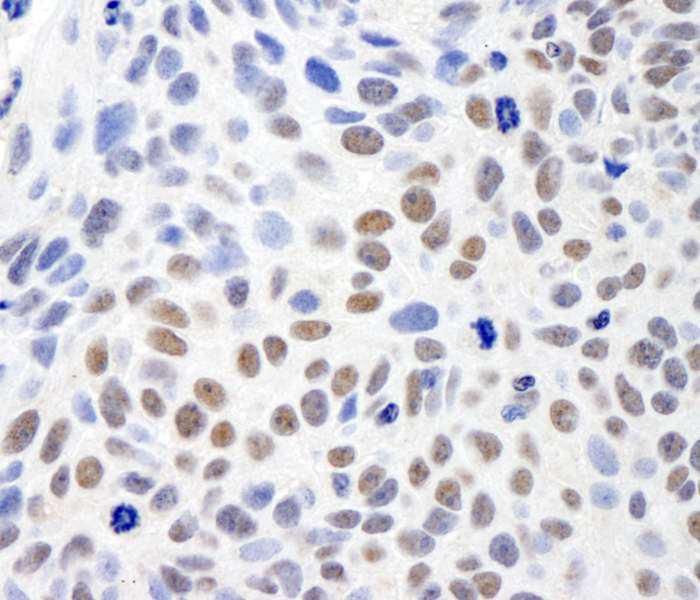
This antibody binds to the structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 1 (SMC1). SMC1 is part of the cohesion complex and involved in chromosome cohesion during cell cycle and in DNA repair. More precisely, the cohesion complex forms a ring, which holds the sister chromatids together during mitosis (SMC1A) and meiosis (SMC1B). This Anti-SMC1 antibody is often used to study this complex and possible relations to other cellular processes by western blotting, immunohistochemistry (as seen in the image to the right), and immunoprecipitation.
Anti-Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)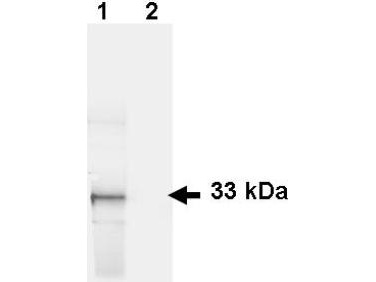
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is one of the most common biomarkers. It is used to visualize cellular processes, localize proteins, and confirm expression of transgenic constructs. Upon excitation with UV or blue light, a bright green fluorescence can be detected. This anti-GFP antibody can be used in a variety of applications to detect or purify different GFP fusion proteins. Methods include immunofluorescence (as seen in the image to the right), immunoprecipitation, and western blotting.
Anti-Mouse EBI-3, clone V1.4C4.22
This monoclonal antibody binds to the protein encoded by the Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3) also known as interleukin-27 (IL-27) subunit β. This subunit forms two different heterodimeric protein complexes: IL-27 [EBI3 + IL27α) and interleukin 35 (IL-35) [EBI3 + IL12α]. IL-27 is involved in T helper cell development and is responsible for differentiation into Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells. IL-35 is involved in immune suppression and therefore linked to autoimmune diseases. Possible applications include ELISAs, western blotting, and immunoprecipitation.
Anti-53BP1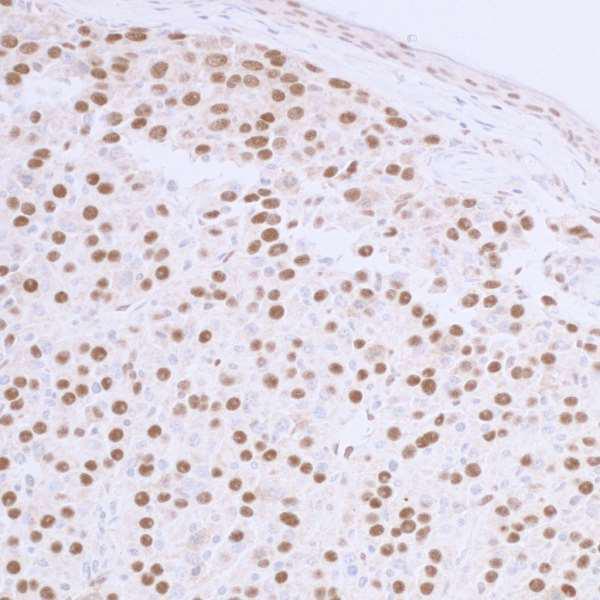
Anti-53BP1 binds to the tumor suppressor p53-binding protein 1 (53BP1). As the name suggests, this protein interacts with p53, one of the most renowned tumor suppressor genes. 53BP1 itself is involved in DNA damage response pathways and promoting non-homologous end joining to fix DNA double-strand breaks. Therefore, this antibody is often used in cancer-related research to monitor undergoing DNA damage in cells.
Rapamycin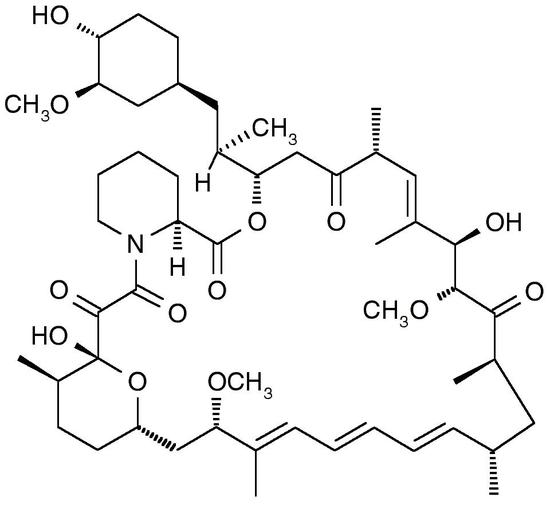
The macrolide rapamycin (also called sirolimus) is best known for inhibiting the protein kinase mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin). This compound forms a complex with the cytosolic protein FKBP12, which in turn targets mTOR. Based on this interaction, rapamycin, in conjunction with FKBP- and mTOR-fusion proteins, is used for chemically induced dimerization (CID). Rapamycin is primarily used as an additive in cell culture to inhibit mTOR and leads to dephosphorylation of downstream proteins like the p70 S6 kinase. Generally, rapamycin is associated with immunosuppressive and antiproliferative properties, but the exact role of rapamycin and mTOR in diseases like cancer and Alzheimer´s is a subject of ongoing research.
Anti-phospho-Kap-1 (Ser824)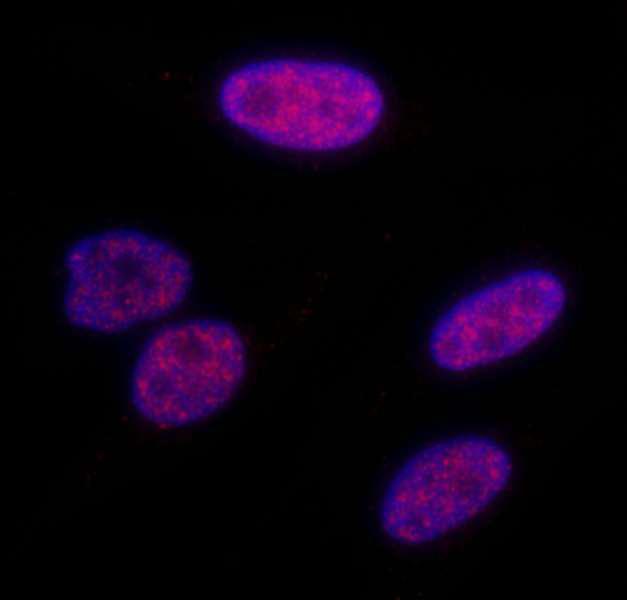
The KRAB-associated protein-1 (KAP-1), also known as TRIM28 or TIF1β, can be detected with this antibody once it has been phosphorylated on serine 824. In vivo, this phosphorylation is catalyzed by the ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) serine kinase upon DNA damage and is assumed to be involved in facilitating DNA repair in damaged chromatin. This antibody can be used to visualize phosphorylated KAP-1 foci in the nucleus by immunofluorescence (as seen in the image to the right). Additional applications include immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and immunoprecipitation.