Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
Organism: Homo sapiens (Human). Source: E.coli. Expression Region: 411-560aa. Protein Length:... more
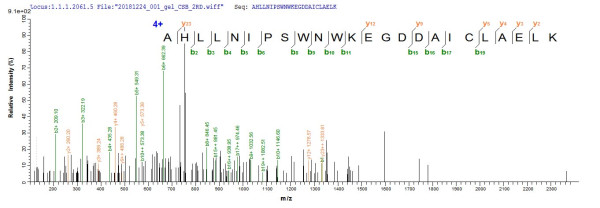
Product information "Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1 (KCNMA1), partial, human, recombinant"
Organism: Homo sapiens (Human). Source: E.coli. Expression Region: 411-560aa. Protein Length: Partial. Tag Info: C-terminal 6xHis-HPC4-tagged. Target Protein Sequence: VVCGHITLES VSNFLKDFLH KDRDDVNVEI VFLHNISPNL ELEALFKRHF TQVEFYQGSV LNPHDLARVK IESADACLIL ANKYCADPDA EDASNIMRVI SIKNYHPKIR IITQMLQYHN KAHLLNIPSW NWKEGDDAIC LAELKLGFIA. Purity: Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE. Endotoxin: Not test. Biological Activity: n/a. Form: Liquid or Lyophilized powder. Buffer: If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0. Reconstitution: We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20 °C/-80 °C. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference. Storage: The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself. Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20 °C/-80 °C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20 °C/-80 °C. Notes: Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4 °C for up to one week. Relevance: Potassium channel activated by both membrane depolarization or increase in cytosolic Ca2+ that mediates export of K+. It is also activated by the concentration of cytosolic Mg2+. Its activation dampens the excitatory events that elevate the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and/or depolarize the cell membrane. It therefore contributes to repolarization of the membrane potential. Plays a key role in controlling excitability in a number of systems, such as regulation of the contraction of smooth muscle, the tuning of hair cells in the cochlea, regulation of transmitter release, and innate immunity. In smooth muscles, its activation by high level of Ca2+, caused by ryanodine receptors in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, regulates the membrane potential. In cochlea cells, its number and kinetic properties partly determine the characteristic frequency of each hair cell and thereby helps to establish a tonotopic map. Kinetics of KCNMA1 channels are determined by alternative splicing, phosphorylation status and its combination with modulating beta subunits. Highly sensitive to both iberiotoxin and charybdotoxin. Reference: "Cloning, expression, and distribution of functionally distinct Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel isoforms from human brain." Tseng-Crank J., Foster C.D., Krause J.D., Mertz R., Godinot N., DiChiara T.J., Reinhart P.H. Neuron 13:1315-1330(1994). Function: Potassium channel activated by both membrane depolarization or increase in cytosolic Ca(2+) that mediates export of K(+). It is also activated by the concentration of cytosolic Mg(2+). Its activation dampens the excitatory events that elevate the cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration and/or depolarize the cell membrane. It therefore contributes to repolarization of the membrane potential. Plays a key role in controlling excitability in a number of systems, such as regulation of the contraction of smooth muscle, the tuning of hair cells in the cochlea, regulation of transmitter release, and innate immunity. In smooth muscles, its activation by high level of Ca(2+), caused by ryanodine receptors in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, regulates the membrane potential. In cochlea cells, its number and kinetic properties partly determine the characteristic frequency of each hair cell and thereby helps to establish a tonotopic map. Kinetics of KCNMA1 channels are determined by alternative splicing, phosphorylation status and its combination with modulating beta subunits. Highly sensitive to both iberiotoxin (IbTx) and charybdotoxin (CTX).
| Keywords: | Slo1, hSlo, MaxiK, KCNMA, KCa1.1, Slo-alpha, BKCA alpha, BK channel, Slo homolog, K(VCA)alpha, Maxi K channel, Slowpoke homolog, Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1, Calcium-activated potassium channel, subfamily M subunit alpha-1, Recombi |
| Supplier: | Cusabio |
| Supplier-Nr: | EP614255HU |
Properties
| Application: | Activity not tested |
| Conjugate: | No |
| Host: | E.coli |
| Species reactivity: | human |
| MW: | 20.0 kD |
| Purity: | >85% (SDS-PAGE) |
Database Information
| KEGG ID : | K04936 | Matching products |
| UniProt ID : | Q12791 | Matching products |
| Gene ID : | GeneID 3778 | Matching products |
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | -20°C |
| Shipping: | +4°C (International: +4°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
You will get a certificate here
Viewed

