Cookie-Einstellungen
Diese Website benutzt Cookies, die für den technischen Betrieb der Website erforderlich sind und stets gesetzt werden. Andere Cookies, die den Komfort bei Benutzung dieser Website erhöhen, der Direktwerbung dienen oder die Interaktion mit anderen Websites und sozialen Netzwerken vereinfachen sollen, werden nur mit Ihrer Zustimmung gesetzt.
Konfiguration
Technisch erforderlich
Diese Cookies sind für die Grundfunktionen des Shops notwendig.
"Alle Cookies ablehnen" Cookie
"Alle Cookies annehmen" Cookie
Ausgewählter Shop
CSRF-Token
Cookie-Einstellungen
FACT-Finder Tracking
Individuelle Preise
Kundenspezifisches Caching
Session
Währungswechsel
Komfortfunktionen
Diese Cookies werden genutzt um das Einkaufserlebnis noch ansprechender zu gestalten, beispielsweise für die Wiedererkennung des Besuchers.
Facebook-Seite in der rechten Blog - Sidebar anzeigen
Merkzettel
Statistik & Tracking
Endgeräteerkennung
Kauf- und Surfverhalten mit Google Tag Manager
Partnerprogramm
Bei Fragen nutzen Sie gerne unser Kontaktformular.
Bestellen Sie auch per E-Mail: info@biomol.com
Größere Menge gewünscht? Bulk-Anfrage
Bestellen Sie auch per E-Mail: info@biomol.com
Größere Menge gewünscht? Bulk-Anfrage
Responsible for the regulation of fatty acid synthesis by phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA... mehr
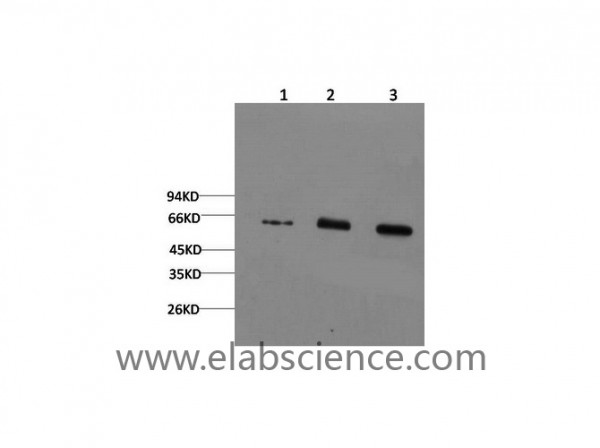
Produktinformationen "Anti-AMPK alpha1, clone 9G3"
Responsible for the regulation of fatty acid synthesis by phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. It also regulates cholesterol synthesis via phosphorylation and inactivation of hormone-sensitive lipase and hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase. Appears to act as a metabolic stress-sensing protein kinase switching off biosynthetic pathways when cellular ATP levels are depleted and when 5'-AMP rises in response to fuel limitation and/or hypoxia. This is a catalytic subunit. Protein function: Catalytic subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an energy sensor protein kinase that plays a key role in regulating cellular energy metabolism (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). In response to reduction of intracellular ATP levels, AMPK activates energy-producing pathways and inhibits energy-consuming processes: inhibits protein, carbohydrate and lipid biosynthesis, as well as cell growth and proliferation (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). AMPK acts via direct phosphorylation of metabolic enzymes, and by longer-term effects via phosphorylation of transcription regulators (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). Regulates lipid synthesis by phosphorylating and inactivating lipid metabolic enzymes such as ACACA, ACACB, GYS1, HMGCR and LIPE, regulates fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis by phosphorylating acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACACA and ACACB) and hormone-sensitive lipase (LIPE) enzymes, respectively. Promotes lipolysis of lipid droplets by mediating phosphorylation of isoform 1 of CHKA (CHKalpha2) (PubMed:34077757). Regulates insulin-signaling and glycolysis by phosphorylating IRS1, PFKFB2 and PFKFB3. AMPK stimulates glucose uptake in muscle by increasing the translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 to the plasma membrane, possibly by mediating phosphorylation of TBC1D4/AS160. Regulates transcription and chromatin structure by phosphorylating transcription regulators involved in energy metabolism such as CRTC2/TORC2, FOXO3, histone H2B, HDAC5, MEF2C, MLXIPL/ChREBP, EP300, HNF4A, p53/TP53, SREBF1, SREBF2 and PPARGC1A (PubMed:11554766, PubMed:11518699, PubMed:15866171, PubMed:17711846, PubMed:18184930). Acts as a key regulator of glucose homeostasis in liver by phosphorylating CRTC2/TORC2, leading to CRTC2/TORC2 sequestration in the cytoplasm. In response to stress, phosphorylates 'Ser-36' of histone H2B (H2BS36ph), leading to promote transcription. Acts as a key regulator of cell growth and proliferation by phosphorylating FNIP1, TSC2, RPTOR, WDR24 and ATG1/ULK1: in response to nutrient limitation, negatively regulates the mTORC1 complex by phosphorylating RPTOR component of the mTORC1 complex and by phosphorylating and activating TSC2 (PubMed:14651849, PubMed:18439900, PubMed:20160076, PubMed:21205641). Also phosphorylates and inhibits GATOR2 subunit WDR24 in response to nutrient limitation, leading to suppress glucose- mediated mTORC1 activation (PubMed:36732624). In response to energetic stress, phosphorylates FNIP1, inactivating the non-canonical mTORC1 signaling, thereby promoting nuclear translocation of TFEB and TFE3, and inducing transcription of lysosomal or autophagy genes (PubMed:37079666). In response to nutrient limitation, promotes autophagy by phosphorylating and activating ATG1/ULK1 (PubMed:21205641). In that process also activates WDR45/WIPI4 (PubMed:28561066). Phosphorylates CASP6, thereby preventing its autoprocessing and subsequent activation (PubMed:32029622). In response to nutrient limitation, phosphorylates transcription factor FOXO3 promoting FOXO3 mitochondrial import. Also acts as a regulator of cellular polarity by remodeling the actin cytoskeleton, probably by indirectly activating myosin (PubMed:17486097). AMPK also acts as a regulator of circadian rhythm by mediating phosphorylation of CRY1, leading to destabilize it. May regulate the Wnt signaling pathway by phosphorylating CTNNB1, leading to stabilize it. Also has tau-protein kinase activity: in response to amyloid beta A4 protein (APP) exposure, activated by CAMKK2, leading to phosphorylation of MAPT/TAU, however the relevance of such data remains unclear in vivo. Also phosphorylates CFTR, EEF2K, KLC1, NOS3 and SLC12A1 (PubMed:20074060, PubMed:12519745). Regulates hepatic lipogenesis. Activated via SIRT3, represses sterol regulatory element- binding protein (SREBP) transcriptional activities and ATP-consuming lipogenesis to restore cellular energy balance. [The UniProt Consortium]
| Schlagworte: | Anti-AMPK1, Anti-PRKAA1, Anti-HMGCR kinase, Anti-ACACA kinase, Anti-AMPK subunit alpha-1, Anti-Tau-protein kinase PRKAA1, Anti-Acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase, Anti-Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase, AMPK alpha1 Monoclonal Antibody |
| Hersteller: | Elabscience |
| Hersteller-Nr: | E-AB-22248 |
Eigenschaften
| Anwendung: | WB, IHC (paraffin) |
| Antikörper-Typ: | Monoclonal |
| Klon: | 9G3 |
| Konjugat: | No |
| Wirt: | Mouse |
| Spezies-Reaktivität: | human, mouse, rat |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant Protein of AMPKalpha1 of PRKAA1 |
| Format: | Purified |
Datenbank Information
| KEGG ID : | K07198 | Passende Produkte |
| UniProt ID : | Q13131 | Passende Produkte |
| Gene ID | GeneID 5562 | Passende Produkte |
Handhabung & Sicherheit
| Lagerung: | -20°C |
| Versand: | -20°C (International: -20°C) |
Achtung
Nur für Forschungszwecke und Laboruntersuchungen: Nicht für die Anwendung im oder am Menschen!
Nur für Forschungszwecke und Laboruntersuchungen: Nicht für die Anwendung im oder am Menschen!
Hier folgen Informationen zur Produktreferenz.
mehr
Hier kriegen Sie ein Zertifikat
Loggen Sie sich ein oder registrieren Sie sich, um Analysenzertifikate anzufordern.
Bewertungen lesen, schreiben und diskutieren... mehr
Kundenbewertungen für "Anti-AMPK alpha1, clone 9G3"
Bewertung schreiben
Loggen Sie sich ein oder registrieren Sie sich, um eine Produktbewertung abzugeben.
Zuletzt angesehen