Cookie-Einstellungen
Diese Website benutzt Cookies, die für den technischen Betrieb der Website erforderlich sind und stets gesetzt werden. Andere Cookies, die den Komfort bei Benutzung dieser Website erhöhen, der Direktwerbung dienen oder die Interaktion mit anderen Websites und sozialen Netzwerken vereinfachen sollen, werden nur mit Ihrer Zustimmung gesetzt.
Konfiguration
Technisch erforderlich
Diese Cookies sind für die Grundfunktionen des Shops notwendig.
"Alle Cookies ablehnen" Cookie
"Alle Cookies annehmen" Cookie
Ausgewählter Shop
CSRF-Token
Cookie-Einstellungen
FACT-Finder Tracking
Individuelle Preise
Kundenspezifisches Caching
Session
Währungswechsel
Komfortfunktionen
Diese Cookies werden genutzt um das Einkaufserlebnis noch ansprechender zu gestalten, beispielsweise für die Wiedererkennung des Besuchers.
Facebook-Seite in der rechten Blog - Sidebar anzeigen
Merkzettel
Statistik & Tracking
Endgeräteerkennung
Kauf- und Surfverhalten mit Google Tag Manager
Partnerprogramm
| Artikelnummer | Größe | Datenblatt | Manual | SDB | Lieferzeit | Menge | Preis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSJ-R31640 | 100 µg | - | - |
3 - 10 Werktage* |
772,00 €
|
Bei Fragen nutzen Sie gerne unser Kontaktformular.
Bestellen Sie auch per E-Mail: info@biomol.com
Größere Menge gewünscht? Bulk-Anfrage
Bestellen Sie auch per E-Mail: info@biomol.com
Größere Menge gewünscht? Bulk-Anfrage
0.5mg/ml if reconstituted with 0.2ml sterile DI water. Calcium-activated potassium channel... mehr
Produktinformationen "Anti-BK channel (KCNMA1)"
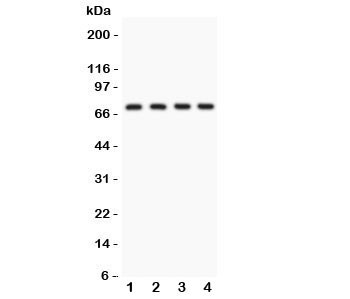
0.5mg/ml if reconstituted with 0.2ml sterile DI water. Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1 also known as KCa1.1, BK channel and Maxi K, is a voltage gated potassium channel encoded by the KCNMA1 gene and characterized by its large conductance of potassium ions (K+) through cell membranes. This gene is located on 10q22.3. BK channels are activated (opened) by changes in membrane electrical potential and/or by increases in concentration of intracellular calcium ion (Ca2+). They are essential for the regulation of several key physiological processes including smooth muscle tone and neuronal excitability. BK channels also contribute to the behavioral effects of ethanol in the worm C. elegans under high concentrations (> 100 mM, or approximately 0.50% BAC). It remains to be determined if they contribute to intoxication in humans. Protein function: Potassium channel activated by both membrane depolarization or increase in cytosolic Ca(2+) that mediates export of K(+) (PubMed:29330545, PubMed:31152168). It is also activated by the concentration of cytosolic Mg(2+). Its activation dampens the excitatory events that elevate the cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration and/or depolarize the cell membrane. It therefore contributes to repolarization of the membrane potential. Plays a key role in controlling excitability in a number of systems, such as regulation of the contraction of smooth muscle, the tuning of hair cells in the cochlea, regulation of transmitter release, and innate immunity. In smooth muscles, its activation by high level of Ca(2+), caused by ryanodine receptors in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, regulates the membrane potential. In cochlea cells, its number and kinetic properties partly determine the characteristic frequency of each hair cell and thereby helps to establish a tonotopic map. Kinetics of KCNMA1 channels are determined by alternative splicing, phosphorylation status and its combination with modulating beta subunits. Highly sensitive to both iberiotoxin (IbTx) and charybdotoxin (CTX). [The UniProt Consortium]
| Schlagworte: | Anti-hSlo, Anti-Slo1, Anti-KCNMA, Anti-MaxiK, Anti-KCa1.1, Anti-Slo-alpha, Anti-BKCA alpha, Anti-BK channel, Anti-K(VCA)alpha, Anti-Slo homolog, Anti-Maxi K channel, Anti-Slowpoke homolog, Anti-Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1, BK chann |
| Hersteller: | NSJ Bioreagents |
| Hersteller-Nr: | R31640 |
Eigenschaften
| Anwendung: | WB, IHC (paraffin) |
| Antikörper-Typ: | Polyclonal |
| Konjugat: | No |
| Wirt: | Rabbit |
| Spezies-Reaktivität: | human, mouse, rat |
| Immunogen: | Human partial recombinant protein (AA 124-467 of KCNMA1) |
| Format: | Purified |
Datenbank Information
| KEGG ID : | K04936 | Passende Produkte |
| UniProt ID : | Q12791 | Passende Produkte |
| Gene ID : | GeneID 3778 | Passende Produkte |
Handhabung & Sicherheit
| Lagerung: | +4°C |
| Versand: | +4°C (International: +4°C) |
Achtung
Nur für Forschungszwecke und Laboruntersuchungen: Nicht für die Anwendung im oder am Menschen!
Nur für Forschungszwecke und Laboruntersuchungen: Nicht für die Anwendung im oder am Menschen!
Hier folgen Informationen zur Produktreferenz.
mehr
Hier kriegen Sie ein Zertifikat
Loggen Sie sich ein oder registrieren Sie sich, um Analysenzertifikate anzufordern.
Bewertungen lesen, schreiben und diskutieren... mehr
Kundenbewertungen für "Anti-BK channel (KCNMA1)"
Bewertung schreiben
Loggen Sie sich ein oder registrieren Sie sich, um eine Produktbewertung abzugeben.
Zuletzt angesehen