Cookie preferences
This website uses cookies, which are necessary for the technical operation of the website and are always set. Other cookies, which increase the comfort when using this website, are used for direct advertising or to facilitate interaction with other websites and social networks, are only set with your consent.
Configuration
Technically required
These cookies are necessary for the basic functions of the shop.
"Allow all cookies" cookie
"Decline all cookies" cookie
CSRF token
Cookie preferences
Currency change
Customer-specific caching
FACT-Finder tracking
Individual prices
Selected shop
Session
Comfort functions
These cookies are used to make the shopping experience even more appealing, for example for the recognition of the visitor.
Note
Show the facebook fanpage in the right blod sidebar
Statistics & Tracking
Affiliate program
Conversion and usertracking via Google Tag Manager
Track device being used
COVID-19 Research
| Item number | Size | Datasheet | Manual | SDS | Delivery time | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KPA-3913 | 1 kit | - | - |
6 - 10 business days* |
344.00€
|
If you have any questions, please use our Contact Form.
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
You can also order by e-mail: info@biomol.com
Larger quantity required? Request bulk
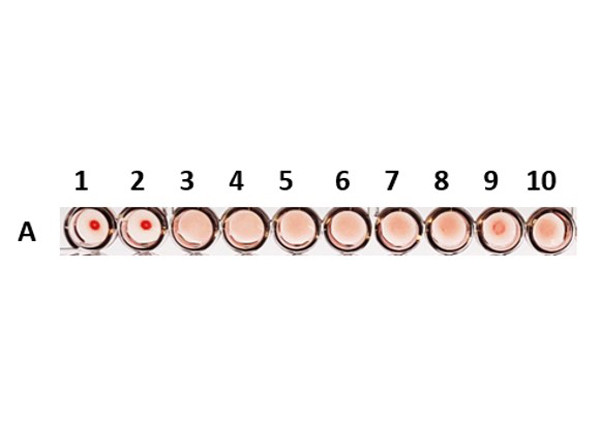
Hemagglutination method is used for titer evaluation of viruses (e.g. Influenza, COVID-19 etc.),... more
Product information "Sheep Hemagglutination Kit"
Hemagglutination method is used for titer evaluation of viruses (e.g. Influenza, COVID-19 etc.), bacteria (e.g. Staphylococci, Shigella etc.), proteins (e.g. certain glycoproteins such as Lectins) and other agents which have the ability to attach to red blood cells (RBC)'s surface molecules. For example, the influenza viruses agglutinate RBCs through their interaction with sialic acid receptors on the host cells. At a molecular level, viral hemagglutinins bind to sialic acid linked to galactose residues through alpha 2.3 or 2.6 linkage, which varies from species to species. Once a hemagglutinin agglutinates the RBCs, each of the agglutinating molecule attaches to RBCs to form a lattice-structure or a meshwork. This prevents RBCs from settling down from suspension in a round bottom 96 well plate. Visually, a hemagglutinated sample will generate a uniform red colored suspension while a sample lacking hemagglutination will lead to settling down of RBCs to the bottom of wells to form button or dot shape. In viral hemagglutination assay, a virus dilution (e.g. 2-fold from 1:4 to 1:4096) will be applied to an RBC dilution (e.g. 0.05% -0.1%) for 30 minutes to an hour at room temperature or 4° C. Thereafter, lattice formation is observed and the titer of a hemagglutination assay can be determined by the last viable "lattice" structure found. If diluted further, the amount of Virus particles will be less than the RBCs and thus not be able to agglutinate them. A Hemagglutination-inhibition (HAI) assay will involve titration of the viral hemagglutination with an anti-viral antibody (often from serum of human or animal infected with that virus) for inhibition of hemagglutination (i.e. neutralization of virus). HAI is one of the most commonly used methods to quantify immunity from influenza and other respiratory viral disease vaccines and is considered the gold standard as a correlate of vaccination mediated protection. Anti-SHEEP Red Blood Cell (RBC) (RABBIT) Antibody - 213-4139-0002 is an IgG fraction antibody purified from polyspecific antiserum by a multi-step process which includes delipidation, salt fractionation and ion exchange chromatography followed by extensive dialysis against the buffer stated above. SHEEP RED BLOOD CELLS (RBC) 10% Washed Pooled Cells - R405-0005 are supplied as a 10 percent suspension in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). 10X Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) consists of 0.2 M Potassium Phosphate, 1.5 M Sodium Chloride, pH 7.2 prepared in highly polished pharmaceutical grade water (WFI). Hemagglutination method is used for titer evaluation of viruses (e.g. Influenza, COVID-19 etc.), bacteria (e.g. Staphylococci, Shigella etc.), proteins (e.g. certain glycoproteins such as Lectins) and other agents which have the ability to attach to red blood cells (RBC)'s surface molecules. For example, the influenza viruses agglutinate RBCs through their interaction with sialic acid receptors on the host cells. At a molecular level, viral hemagglutinins bind to sialic acid linked to galactose residues through alpha 2.3 or 2.6 linkage, which varies from species to species. Once a hemagglutinin agglutinates the RBCs, each of the agglutinating molecule attaches to RBCs to form a lattice-structure or a meshwork. This prevents RBCs from settling down from suspension in a round bottom 96 well plate. Visually, a hemagglutinated sample will generate a uniform red colored suspension while a sample lacking hemagglutination will lead to settling down of RBCs to the bottom of wells to form button or dot shape. In viral hemagglutination assay, a virus dilution (e.g. 2-fold from 1:4 to 1:4096) will be applied to an RBC dilution (e.g. 0.05% -0.1%) for 30 minutes to an hour at room temperature or 4° C. Thereafter, lattice formation is observed and the titer of a hemagglutination assay can be determined by the last viable "lattice" structure found. If diluted further, the amount of Virus particles will be less than the RBCs and thus not be able to agglutinate them. A Hemagglutination-inhibition (HAI) assay will involve titration of the viral hemagglutination with an anti-viral antibody (often from serum of human or animal infected with that virus) for inhibition of hemagglutination (i.e. neutralization of virus). HAI is one of the most commonly used methods to quantify immunity from influenza and other respiratory viral disease vaccines and is considered the gold standard as a correlate of vaccination mediated protection.
| Supplier: | Rockland Immunochemicals |
| Supplier-Nr: | KPA-3913 |
Properties
| Host: | Sheep |
Database Information
Handling & Safety
| Storage: | +4°C |
| Shipping: | +4°C (International: +4°C) |
Caution
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Our products are for laboratory research use only: Not for administration to humans!
Information about the product reference will follow.
more
You will get a certificate here
Viewed